Electric vehicles could fully recharge in under 5 minutes with new charging station cable design
Purdue University engineers have invented a new, patent-pending charging station cable that would fully recharge certain electric vehicles in under five minutes – about the same amount of time it takes to fill up a gas tank.
Today, chargers are limited in how quickly they can charge an EV’s battery due to the danger of overheating. To charge an EV faster, a higher current needs to travel through the charging cable. The higher the current, the greater amount of heat that must be removed to keep the charging cable operational. The cooling systems that chargers currently use remove only so much heat.
Using an alternative cooling method, Purdue researchers designed a charging cable that can deliver a current 4.6 times that of the fastest available EV chargers on the market today by removing up to 24.22 kilowatts of heat. The project was funded by a research and development alliance between Ford Motor Co. and Purdue.
Electric vehicle charging time can vary widely today, from 20 minutes at a station alongside a roadway to hours using an at-home charging station. Wait times and charger location are both cited as major sources of anxiety for people who are considering electric vehicle ownership.
“My lab specializes in coming up with solutions for situations where the amounts of heat that are produced are way beyond the capabilities of today’s technologies to remove,” said Issam Mudawar, Purdue’s Betty Ruth and Milton B. Hollander Family Professor of Mechanical Engineering.

“Ford is committed to making the transition to electrification easy,” said Matt Stover, director of charging, energy services and business development at Ford. “We are glad to support Purdue’s research, which has the potential to make electric vehicle and commercial fleet ownership more appealing and accessible.”
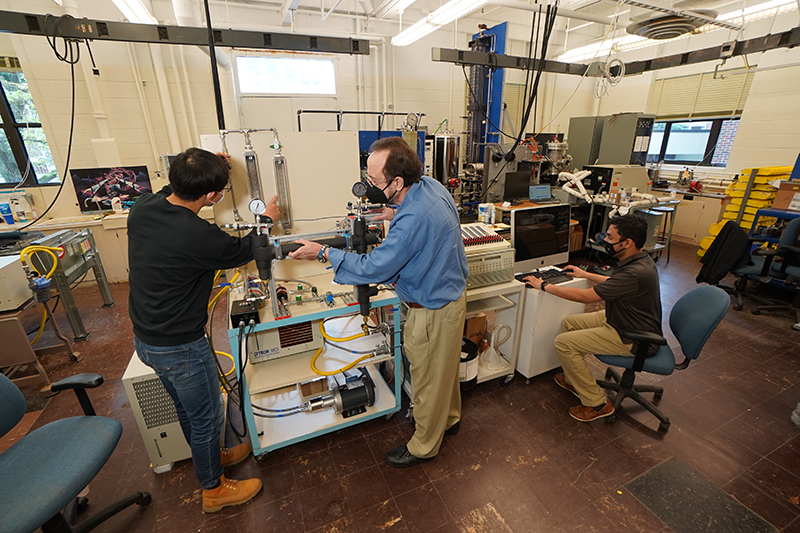
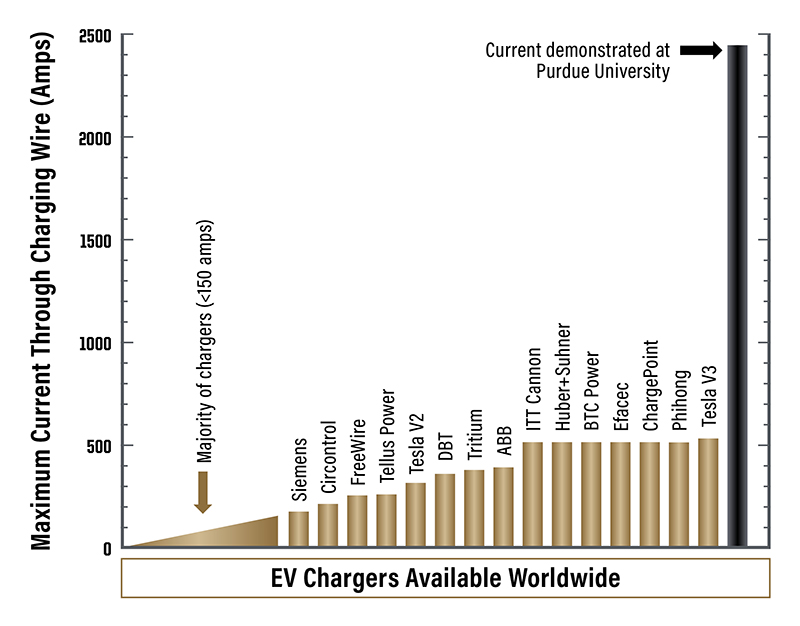
Though the prototype hasn’t been tested on EVs yet, Mudawar and his students demonstrated in the lab that their prototype accommodates a current of over 2,400 amperes – far beyond the 1,400-ampere minimum that would be needed to reduce charging times for large commercial EVs to five minutes. The most advanced chargers in the industry deliver only currents up to 520 amperes, and most chargers available to consumers support currents of less than 150 amperes.
Ultimately, charge times will be dependent on the power output ratings of the power supply and charging cable, and the power input rating of the EV’s battery. To obtain a sub-five minute charge, all three components will need to be rated to 2,500 amperes.
The prototype also mimics all the traits of a real-world charging station: It includes a pump, a tube with the same diameter as an actual charging cable, the same controls and instrumentation, and it has the same flow rates and temperatures.
Mudawar’s lab intends to work with EV or charging cable manufacturers to test the prototype on EVs within the next two years. The testing will determine more details on charge speeds for specific models of EVs. A video about the project is available on YouTube.
Removing more heat to shorten EV charging time
EV charging stations and other types of electronics rely on liquid cooling systems to remove heat from within their wires. Increasing the current through a charging cable using this method would require larger conductive wires and more liquid coolant, making the cable heavier and difficult for customers to handle.
For the past 37 years, Mudawar has been developing ways to more efficiently cool electronics by taking advantage of how liquid captures heat when boiled into a vapor. By capturing heat in both liquid and vapor forms, a liquid-to-vapor cooling system can remove at least 10 times more heat than pure liquid cooling.
These cooling benefits make it possible to use a smaller wire diameter inside the charging cable while dissipating a higher current. Research papers on the team’s experimental demonstration of the charging cable prototype and the cooling method it uses have been published in the International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer.
Despite decades of research on liquid-to-vapor cooling, no industry has begun using these systems yet because studies like those conducted by Mudawar’s lab are needed to understand how to best implement the technology.
“The industry has a gap in knowledge and expertise needed to switch from pure liquid cooling to liquid phase change cooling. How do you design the system? What type of equations do you use to optimize it? But we do have this knowledge through our extensive research,” Mudawar said.
Beyond EVs: aircraft and spacecraft
Based on what Mudawar and his students observed from experimental demonstrations of their prototype, liquid-to-vapor cooling is so effective at removing large amounts of heat that EVs could charge in far less than five minutes using this technology.
“The industry doesn’t really need EVs to charge faster than five minutes, but we think we can increase the current even more by modifying both the state of the incoming liquid and the design of the cooling space around the conductor wires in the charging cable,” Mudawar said.
The prototype’s ability to remove far more heat than other chargers wasn’t a surprise to Mudawar. “My lab has developed solutions using liquid phase change technology for many applications, including in aerospace and defense. We knew how capable the technology is,” he said.
Similar to the EV charging cable prototype, the systems that Mudawar’s lab has designed for aircraft allow avionics to dissipate great amounts of heat, increasing their performance. Mudawar also has projects funded by NASA to boost the cooling capabilities of rocket engines and spacecraft.
The researchers have filed a patent application for their charging cable invention through the Purdue Research Foundation Office of Technology Commercialization and are seeking additional industry partners to continue the technology’s development.
ABSTRACTS
Consolidated theoretical/empirical predictive method for subcooled flow boiling in annuli with reference to thermal management of ultra-fast electric vehicle charging cables
V.S. Devahdhanush, Seunghyun Lee, Issam Mudawar
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2021.121224
Ability to deliver very high electrical current through a charging cable is key to successful proliferation of electric vehicles (EVs). Associated with high current delivery is a host of thermal problems stemming from the need to remove enormous amounts of heat from the cable. This study seeks to develop a highly effective thermal management scheme based on subcooled flow boiling principles. The main objective is to develop a consolidated theoretical/empirical method for predicting the heat transfer and pressure drop characteristics of both laminar and turbulent flows though concentric circular annuli with uniformly heated inner wall and adiabatic outer wall. Although maintaining subcooled boiling along the entire cable is a key practical objective, this consolidated method is shown to be capable of tackling multiple flow regimes (single-phase liquid, subcooling boiling, saturated boiling, and single-phase vapor) and highly effective at predicting local surface and fluid temperatures. This method is then adopted to design and optimization of very high current EV charging cable cooling system using dielectric fluid HFE-7100 as coolant. Effects of various parameters, including electrical current, both wire and conduit sizes, inlet fluid temperature, and flow rate are carefully addressed and recommendations made for effective and robust overall system design.
Experimental investigation of subcooled flow boiling in annuli with reference to thermal management of ultra-fast electric vehicle charging cables
V.S. Devahdhanush, Seunghyun Lee, Issam Mudawar
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2021.121176
Transportation industry is presently in fast track to transition from Internal Combustion Engine Vehicles (ICEVs) to Electrical Vehicles (EVs). One of the most pressing challenges to full adoption of EVs is very slow charging at the networks of charging stations proposed worldwide. Despite many recent so-called ‘ultra-fast’ charging methods, which capitalize on a variety of single-phase liquid schemes to cool the charging cable, thermal constraints limit the electrical current carrying capacity of the fastest commercial chargers to about 500 A. Achieving the faster charging time required for the anticipated proliferation of EVs will require increasing this current capacity to at least 2000 A, which poses formidable thermal challenges in design of the charging cable. This study explores the development of a vastly more powerful charging cable thermal management scheme to achieve this higher current threshold. Subcooled flow boiling is proposed as the primary means to dissipating the larger amounts of heat generated at higher currents. Experiments are performed by pumping highly subcooled dielectric liquid HFE-7100 though a concentric circular annulus mimicking a segment of an actual cable, with a uniformly heated 6.35-mm-diameter inner surface representing the electrical conductor and adiabatic 23.62-mm-diameter outer surface the external conduit. All experimental cases considered are conFig.d to ensure subcooled fluid conditions throughout the test module. It is shown the proposed cooling scheme is capable of tackling currents up to 2438 A, around four times higher than the present-day commercial maximum. With appropriate batteries and other ancillary components, this technology is expected to bring EV charging times down to less than 5 minutes. Aside from demonstrating this potential, an assessment of available subcooled boiling heat transfer coefficient correlations identified Moles and Shaw’s to predict the new experimental data with an overall mean absolute error of only 11.68%. The flow and heat transfer physics are also explained in detail.








